Comparison of solvers for Poisson regression¶
In this example, we explain how to try out different solvers for the Poisson
regression model, using \(\ell_2^2\) penalization, namely ridge (which is
the default value for the penalty parameter in
tick.inference.PoissonRegression).
Note that for this learner, the step of the solver cannot be tuned
automatically. So, the default value might work, or not.
We therefore urge users to try out different values of the step parameter
until getting good concergence properties.
Other penalizations are available in tick.inference.PoissonRegression:
no penalization, using
penalty='none'\(\ell_1\) penalization, using
penalty='l1'elastic-net penalization (combination of \(\ell_1\) and \(\ell_2^2\), using
penalty='elasticnet', where in this case theelastic_net_ratioparameter should be used as welltotal-variation penalization, using
penalty='tv'
Remark: we don’t use in this example solver='sgd' (namely vanilla
stochastic gradient descent, see tick.solver.SGD) since it performs
too poorly.
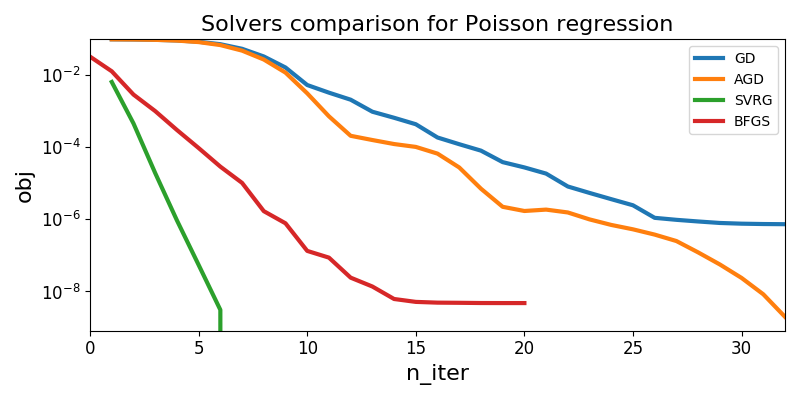
The plot given below compares the distance to the minimum of each solver along iterations, on a logarithmic scale.
Python source code: plot_poisson_regression.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tick.simulation import weights_sparse_gauss
from tick.linear_model import SimuPoisReg, PoissonRegression
from tick.plot import plot_history
n_samples = 50000
n_features = 100
np.random.seed(123)
weight0 = weights_sparse_gauss(n_features, nnz=int(n_features - 1)) / 20.
intercept0 = -0.1
X, y = SimuPoisReg(weight0, intercept0, n_samples=n_samples, verbose=False,
seed=123).simulate()
opts = {'verbose': False, 'record_every': 1, 'tol': 1e-8, 'max_iter': 40}
poisson_regressions = [
PoissonRegression(solver='gd', **opts),
PoissonRegression(solver='agd', **opts),
PoissonRegression(solver='svrg', random_state=1234, **opts),
PoissonRegression(solver='bfgs', **opts)
]
for poisson_regression in poisson_regressions:
poisson_regression.fit(X, y)
plot_history(poisson_regressions, log_scale=True, dist_min=True)
plt.title('Solvers comparison for Poisson regression', fontsize=16)
plt.tight_layout()
Total running time of the example: 11.26 seconds ( 0 minutes 11.26 seconds)